Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a bacterial infection that affects the gums and bone supporting the teeth. It is caused by plaque and tartar buildup on the teeth and can lead to gum recession, tooth loss, and other oral health problems.
Gum Disease Treatment
Gum disease or periodontal disease refers to conditions that affect the supporting tissue of the teeth such as the gums and also the deeper tissues of the bone, root surface and the ligament that connects the teeth to the bone.
Gum disease is caused by the bacteria in plaque. Plaque is a sticky, colourless film that forms on your teeth.
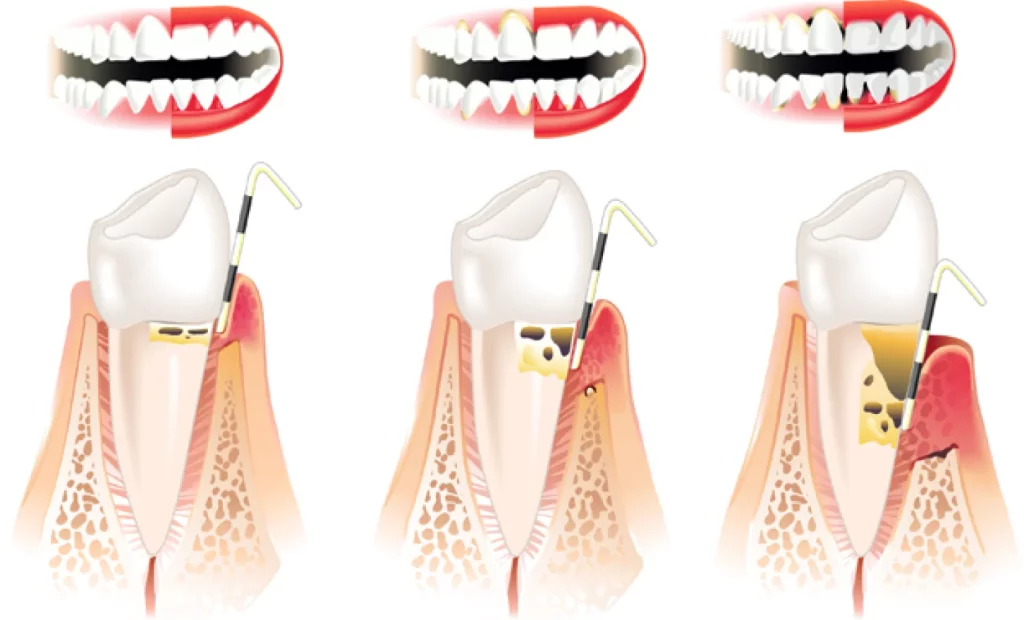
Gingivitis is infection of the surface tissue only. The effects of gingivitis are reversible with appropriate care.
Gingivitis may progress to affect the deeper supporting tissue, this is called Periodontitis.
Periodontitits or periodontal disease results in the destruction of the deeper supporting tissue – the bone and the ligament that connects the tooth to the bone. This destruction results in a space between the gum and the tooth called a pocket. The pocket forms a protective environment for bacteria and the disease progresses resulting in further destruction of bone and ligament until the tooth is lost due to the lack of support to hold it into the bone.
- Risks factor for gum disease
Some people are more at risk of developing periodontal disease due to their family history of the disease. Smoking is also a major risk factor along with other conditions such as diabetes, stress, pregnancy and various medications.
- Signs of gum disease
The most easily recognisable symptom of gum disease is bleeding gums while brushing and flossing. Patients may also experience pain when chewing or be extra sensitive to hot and cold foods if the gums have started to recede. The gums may appear red and inflamed and patients suffering from the condition may suffer from chronic bad breath.
- Treatment of gum disease
In the vast majority of cases the progression of gum disease can be arrested with appropriate care, however management becomes more difficult the more the disease progresses. It is therefore important to diagnose and treat gum disease as early as possible. Gum disease is managed by reducing the bacteria to a level the body’s defence mechanism can handle. This is done by:
• Excellent home care – brushing and flossing (and if advised a medicated mouth rinse)
• Regular professional cleaning of the teeth to remove the plaque and the hard calcified plaque deposits (calculus/tartar)
• Regular reviews
• Reducing risk factors such as smoking
For treatment of periodontitis and gingivitis on the Central Coast see our dentists at Terrigal Beach Dental. We combine the latest techniques with friendly instruction on good oral hygiene that can help you stop the progression of gum disease.
some common treatments for gum disease
- Scaling and root planning
This is a deep cleaning procedure that involves removing plaque and tartar build-up from the teeth and root surfaces, smoothing rough spots on the tooth roots, and removing bacteria that cause gum disease.
- Antibiotics
In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to help eliminate bacterial infections in the gums
- Surgery
In more severe cases of gum disease, surgery may be necessary to remove damaged tissue or to reshape the gums and bone surrounding the teeth.
- Laser therapy
This is a newer treatment option that uses a laser to remove diseased gum tissue and promote healing.
• Prevention is the best treatment for gum disease. Regular dental cleanings, daily brushing and flossing, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can all help prevent gum disease from developing. It's also essential to seek treatment early if you suspect you have gum disease, as early intervention can help prevent further damage to your gums and teeth.

